Various statistics run by health organizations across the globe rank back pain as a global burden. More than 1 in 10 individuals suffer back pain worldwide, making none of the population groups immune to the disability. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates the prevalence of lower back pain at 60%-70% in industrialized countries.
The prevalence rates of back pain are lower in children compared to adults. Notably, adults between the age of 35 and 55 have higher chances of experiencing back pain. Despite multiple measures implemented to reduce the currency of back pain, the symptoms are likely to surge as time unfolds, especially among low and middle-income populations.
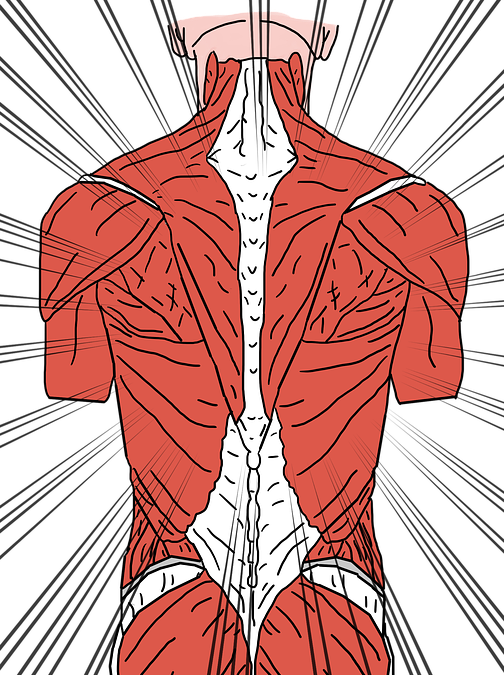
Types of muscles that result in back pain
Did you know that muscles make up to 50% of a person’s body weight? According to most sources, such as White Pine Health, there are approximately 650 muscles in the body. The muscular system is responsible for mobility, stability, posture, circulation, among several other activities.
There are three types of muscles that result in back pain.
| Muscle | Description |
| Extensor muscles |
|
| Flexor muscles |
|
| Oblique muscles |
|
Symptoms of tight back muscles
Some common symptoms associated with tight back muscles include:
- Pulling pain in the area of the lumbar spine
- The pain usually ranges from minor to severe
- Restricted mobility
- Cramping and stiffness
How tight muscles cause back pain
As previously mentioned, muscles in the back expand or contract to facilitate the movement of tissues associated with the back. The long and slender cells making up the muscles are collectively responsible for the mobility. The cells are characterized by a network of blood vessels that supply them with essential requirements such as oxygen and water.
If back muscles lack or receive insufficient essential supplies such as oxygen and water, they suffer injury. Additionally, their functionality is compromised. To prevent further damage, muscles constrict, thereby experiencing tension.
Atop the network of blood vessels supplying the muscles with essential implements is a connection of the nervous system to the back muscles. The nervous system is formulated to signal the brain whenever any compromising condition arises in the body. Consequently, when the nervous systems detect signs of injury to the muscles on the back, they send a signal to the brain. It is these signals that result in painful sensations around the damaged area of the back.
Causes of tight muscles that result to back pain
Several reasons associated with tight muscles that lead to back pain include:
- Physical inactivity
- Taking prolonged, uncomfortable postures that put stress on one side of the body.
- Prolonged sitting hours
- Dehydration
- A poor mattress
Ways to cure tight muscles that cause back pain
Various treatment options can be applied to relieve the tension of tight muscles on the back. Physiotherapy is one of the most common options, where local heat treatment is applied to the lumbar region to relieve muscular stress. In case the pain experienced by a patient is acute, physiotherapy is usually accompanied by medication, especially pain killers.
Another solution to relieving the muscles of tension on the back is carrying out a variety of popular stretches. These include; the knee-to-chest stretch, cat-cow stretch, kneeling lunge stretch, sphinx, piriformis, among several others.
Finally, if back pain persists longer than expected, then you should seek medical advice from your doctor.